In the sixth installment of their series, democracy around the world, NCDD sponsoring member, the Jefferson Center, wrote this piece on how Americans can be more civically engaged and address our challenging issues. Many of the states in the U.S. are designed to give the people even more power to shape legislation through initiatives and referendums. The article challenges for people to push more into civic life and participate in government, especially when their elected officials are not. You can read the article below and find the original version of it on the Jefferson Center site https://jefferson-center.org/2018/09/initiate-democracy-across-the-united-states/here.
It’s Time to Initiate Democracy Across the United States
 This is the sixth post in our blog series exploring democracy around the world, submitted by a diverse group of people interested in using deliberation, participation, and civic tech to solve challenges we face today. The following does not necessarily represent the views of the Jefferson Center or Jefferson Center staff.
This is the sixth post in our blog series exploring democracy around the world, submitted by a diverse group of people interested in using deliberation, participation, and civic tech to solve challenges we face today. The following does not necessarily represent the views of the Jefferson Center or Jefferson Center staff.
John Hakes is a freelance writer and Certified Public Accountant who has worked with the U.S. Census Bureau and Questar Assessment Inc. He earned his Master’s Degree in Advocacy and Political Leadership from the University of Minnesota Duluth.
Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble, and to petition the government for a redress of grievances. – First Amendment to the U.S. Constitution
In the opening blog of this series, guest blogger Ross Busch suggested a national assembly model recently employed by the country of Ireland– on an agenda of climate change leadership, aging population and abortion– might be used to address the seemingly intractable issue of gun control in the United States.
If Ireland, a nation with a centuries-long entrenched position on the sensitive abortion issue can use informed reasoning to assess the will of the people through assembly— the Busch reasoning goes– there is hope people could do likewise on other emotionally-charged issues.
We will now ‘wait ‘n see’ whether Busch’s clarion call takes root around the world. But meanwhile, in November, the twin ‘people power’ petition mechanism afforded to American citizens by the First Amendment will be exercised on the issue of gun control. That’s when Washington citizens will decide whether they wish to add parameters to the use of firearms through a vote of the people via Initiative I-1639.
The Initiative Tool
Should you call states like Hawaii, New Mexico, Iowa, North Carolina, Maryland, or around 20 others home, you may not be not familiar with the initiative process.
Unlike a referendum, where a question must come from a given jurisdiction’s legislative body, a citizen initiative is typically created when a certain number of ‘registered voter’ signatures are gathered on a question proposed to become law. Initiatives can either be direct (where potential new law is decided on by voters) or indirect (where the affirmed petition question is handed to a Legislature for it to decide on).
The state of Washington’s citizen initiative process was enacted in 1897. The I-1639 effort began when the gun measure petition received the requisite number of signatures from across the state. Naturally, the road from ‘obtaining a verifiable set of signatures’ to ‘Secretary of State approval’ to ‘finalized question on the November ballot’ has been met by significant counter challenges. But on August 24, 2018, a ruling of the Washington Supreme Court officially permitted the existence of the ‘gun measures’ question to be included on the November 6th ballot .
Initiative and Referendum in the U.S.
Less than half of the U.S. states allow their citizens to raise & legally install the answer to a question through the initiative process. More western than eastern states have this process in place.
At least partly due to the continually shifting voting preferences over time in a given electorate, states currently deemed ‘red’ and ‘blue’ both offer legislation-by-initiative. Washington & California are examples of so-called blue states while North Dakota and Arizona are counted among ‘red’ states that utilize initiatives.
Unsurprisingly, voter turnout in these states has historically been 5 to 7 percent higher than in states without initiative and referendum (states with one typically offer the other). The reason for this is simple: voters feel that their vote for or against a grassroots-raised issue on the ballot does make a difference.
Despite being a state that frequently leads the nation in voter turnout, Minnesota–also well-known for possessing a strong political and civic culture–features neither an Initiative or Referendum component in its democratic procedural toolkit.
Like every other state, Minnesota does allow questions pertaining to legislatively-referred, state constitutional amendments to be decided on by voters. There have been three periods in which the right to decide by Initiative has been seriously considered in Minnesota, with the last push led by MN House Representative Erik Paulsen during the Jesse Ventura administration of the early 2000s.
Looking ahead
Although it’s true that social media has the power to amplify voices and mobilize people to achieve ‘a’ form of grassroots push on a given issue, such sentiments too often blow away with the wind of the next incoming news cycle. Rather than focusing only on the couch-potato democracy by electronic device, Americans in half of the U.S. states should exercise the legal levers they already have to permanently alter the law when their elected representatives don’t seem up to the task.
To quote the Busch piece again: “Conversations between ordinary citizens on complex topics are perhaps the greatest defense against the degradation of modern politics.”
What better way to begin stepping across the street for face-to-face conversation than to create outcomes on even an incredibly divisive issue through an Initiative provision, like approximately half of our country’s people have the legal luxury of doing?
And though founders like James Madison would likely be one to equate the Initiative process with ill-advisedly caving to the passions of the people, perhaps even our celebrated ‘Father of the Constitution’ might see the diligence and organization required of Initiative efforts as preferable to the Rule by Retweet method that regularly influences the course of events today.
Thanks to efforts like those who’ve advanced the I-1639 in Washington, political pockets of our country are arguably “deliberating, even when it’s difficult,” on important issues, as writer Ross Busch recommends.
You can find the original version of this article on The Jefferson Center site at www.jefferson-center.org/2018/09/initiate-democracy-across-the-united-states/.

 We lift up the biggest lessons below…
We lift up the biggest lessons below…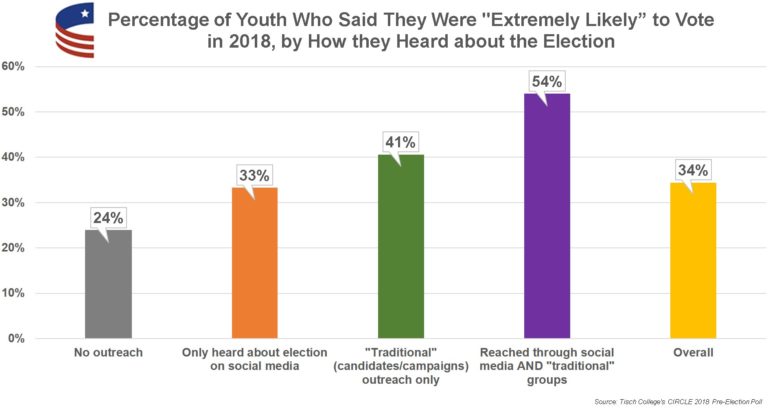
 NCDD envisions a future in which all people–regardless of income, position, background or education–are able to engage regularly in lively, thoughtful, and challenging discussions about what really matters to them, in ways that have a positive impact on their lives and their world. We envision a society in which systems and structures support and advance inclusive, constructive, dialogue and deliberation.
NCDD envisions a future in which all people–regardless of income, position, background or education–are able to engage regularly in lively, thoughtful, and challenging discussions about what really matters to them, in ways that have a positive impact on their lives and their world. We envision a society in which systems and structures support and advance inclusive, constructive, dialogue and deliberation. For sixteen years, NCDD has worked hard to gather visionaries and practitioners dedicated to raising the quality of discourse across many key issues and questions. Many of you have been a part of that – and we’re grateful for you!
For sixteen years, NCDD has worked hard to gather visionaries and practitioners dedicated to raising the quality of discourse across many key issues and questions. Many of you have been a part of that – and we’re grateful for you! Following the 2016 election, Democracy Fund heard from many philanthropists seeking advice on what they can do to respond to the threats facing our political system. For some, the last two years have brought a newly pervasive sense that our democracy is under threat and that our political system is far more fragile than most of us assumed. We feel the same way, and we are humbled that interested donors and their advisors are turning to us and to our peers for guidance.
Following the 2016 election, Democracy Fund heard from many philanthropists seeking advice on what they can do to respond to the threats facing our political system. For some, the last two years have brought a newly pervasive sense that our democracy is under threat and that our political system is far more fragile than most of us assumed. We feel the same way, and we are humbled that interested donors and their advisors are turning to us and to our peers for guidance.

 This is the sixth post in our blog series exploring democracy around the world, submitted by a diverse group of people interested in using deliberation, participation, and civic tech to solve challenges we face today. The following does not necessarily represent the views of the Jefferson Center or Jefferson Center staff.
This is the sixth post in our blog series exploring democracy around the world, submitted by a diverse group of people interested in using deliberation, participation, and civic tech to solve challenges we face today. The following does not necessarily represent the views of the Jefferson Center or Jefferson Center staff.