The six-page article, “The International Residents Network: A Self-Sustaining Instrument for Learning and Sharing” by Ruby Quantson was published in Kettering Foundation‘s 2016 edition of their annual newsletter, Connections – Kettering’s Multinational Research. In the ninth article of the newsletter, Quantson talks about her efforts to re-connect with members of Kettering’s International Residents Network. She and Leonardo Correa, a previous member of the network reached out to fellow members to see in what ways the network had been self-sustained and what to do moving forward. Below is an excerpt from the article and Connections 2016 is available for free PDF download on Kettering’s site here.
From the article…

Responding to growing international interest in democracy research, in 1991, the Kettering Foundation established international residencies. These residencies, initially called “fellowships,” include the international residents, the Katherine W. Fanning Residents in Journalism and Democracy, and staff exchanges with the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences and Peking University. Residents usually spend several months at the foundation’s headquarters in Dayton, Ohio, exploring questions central to Kettering’s research program. Thus far, about 130 people have participated from around the world.
In the spring of 2014, I embarked, along with Leonardo Correa from Brazil, on a new research project to locate as many former international residents as we could. Both of us are former international residents, which put us in a unique position to interview others and analyze what we heard. This article focuses on the insights gathered from the research, expressed through the thoughts and voices of those we interviewed. It particularly highlights existing foundations and structures for building a formidable international network and how this platform could be sustained for learning across the world through self-responsibility as a principle of democratic practice.
A key interest in this research was whether former residents (at least a critical number) were self-motivated enough to be responsible for sustaining the network. This interest was particularly driven by two questions posed in the research interviews: how might you work with the international network, and how can the network be managed and sustained?
Mapping out Opportunities for Networking
Interactive Database
The core product generated in this research, critical to the sustenance of the network, was a database or directory on former residents. Intended to operate as an online interactive map, the directory describes careers, interests, and contact details of former residents and therefore offers the international alumni a platform to connect, exchange ideas, and promote collaborative work across a broad range of careers. Several former residents are applying the knowledge acquired during their residency in innovative ways. Their stories have the potential to ignite citizens’ actions elsewhere. For instance, a former resident who currently works as a wood sculptor observed inter alia:
I then took a few chairs and tables of wood; I went to a park near my place, . . . I made a circle, then I invited a few friends and the community. A lot of people came, people from my neighborhood, women that worked around the place, some of my students. . . . Now this place is a space where people can get together and talk about their issues.
What is needed is a means of sharing and learning from these experiences.
Global Voices and Actions for Democracy
The conversations with the former residents also revealed a broad knowledge base enriched by diverse cultures, practices, and experiences useful for knowledge exchange and transfer. The thoughts expressed were not abstract or whimsical; it was a rich and pressing struggle. They spoke to us about the challenges to democracy they see or seek to address within the contexts of a world facing a variety of challenges, including ISIS, Al-Shabaab, and Boko Haram; immigration and refugee crises; polarized politics; diminishing roles for NGOs; and coup d’états and unsustainable development goals in the developing world. When these voices and actions come together, they depict a challenging, yet engaging, global effort toward stronger democratic practices. If these conversations were to take place in a regular (even virtual) space among the residents, the learning and insights would be profound.
Building on Existing Initiatives
Former residents are interacting in many ways all around the world. We have learned of small gatherings in Argentina, Brazil, Colombia, Fiji, Ireland, New Zealand, Russia, and Tajikistan, to mention a few.
Residents from Ghana have assisted in offering training programs and participated in programs for organizations led by former residents from Zimbabwe and South Africa. The interactions range from simple dinners to exploring democratic practices in policymaking, as well as naming and framing issues. Several former residents are focused on boundary spanning, collaborating with each other to coproduce civic goods that strengthen democracy and promote learning in their respective institutions, as we heard in Kosovo and Tajikistan.
Mapping out these formal and informal connections with the aim of sharing with the larger network and upscaling can lead to greater learning and sustenance of the network.
This is just an excerpt, you can read the rest of the article by clicking here.
About Kettering Foundation and Connections
 The Kettering Foundation is a nonprofit operating foundation rooted in the American tradition of cooperative research. Kettering’s primary research question is, what does it take to make democracy work as it should? Kettering’s research is distinctive because it is conducted from the perspective of citizens and focuses on what people can do collectively to address problems affecting their lives, their communities, and their nation.
The Kettering Foundation is a nonprofit operating foundation rooted in the American tradition of cooperative research. Kettering’s primary research question is, what does it take to make democracy work as it should? Kettering’s research is distinctive because it is conducted from the perspective of citizens and focuses on what people can do collectively to address problems affecting their lives, their communities, and their nation.
Each issue of this annual newsletter focuses on a particular area of Kettering’s research. The 2016 issue of Connections, edited by KF program officer and senior writer/editor Melinda Gilmore; KF senior associate Philip Stewart; and KF vice president, secretary, and general counsel Maxine Thomas, focuses on our year-long review of our multinational research.
Follow on Twitter:
Resource Link: www.kettering.org/sites/default/files/periodical-article/Quantson-Connections-2016.pdf
 Areas of interest and application for the course will include:
Areas of interest and application for the course will include: Democracy and Leadership: On Pragmatism and Virtue (Lanham, MD: Lexington Books, 2013)
Democracy and Leadership: On Pragmatism and Virtue (Lanham, MD: Lexington Books, 2013) Uniting Mississippi: Democracy and Leadership in the South (Jackson, MS: The University Press of Mississippi, 2015)
Uniting Mississippi: Democracy and Leadership in the South (Jackson, MS: The University Press of Mississippi, 2015) In addition, for those who are unfamiliar, I co-host the Philosophy Bakes Bread radio show & podcast that airs on WRFL Lexington, 88.1 FM and in the show we cover a number of public policy topics. Give it a listen!
In addition, for those who are unfamiliar, I co-host the Philosophy Bakes Bread radio show & podcast that airs on WRFL Lexington, 88.1 FM and in the show we cover a number of public policy topics. Give it a listen!





 The Better Arguments Project allows Americans to reach across political, cultural and economic divides to have arguments that bring us closer together instead of driving us further apart. We launched this project out of the recognition that arguments are essential for our democracy. Indeed, America is an argument — between equality and liberty, central and local government, unity and diversity. The more we can equip communities to have arguments rooted both in this history and in best practices of constructive communication, the healthier our country will be.
The Better Arguments Project allows Americans to reach across political, cultural and economic divides to have arguments that bring us closer together instead of driving us further apart. We launched this project out of the recognition that arguments are essential for our democracy. Indeed, America is an argument — between equality and liberty, central and local government, unity and diversity. The more we can equip communities to have arguments rooted both in this history and in best practices of constructive communication, the healthier our country will be.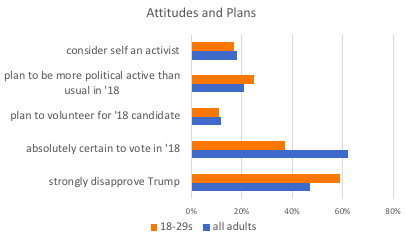
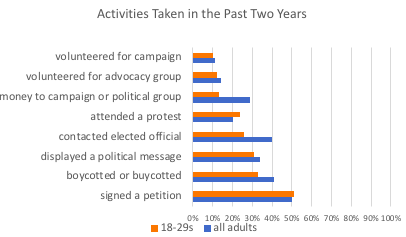
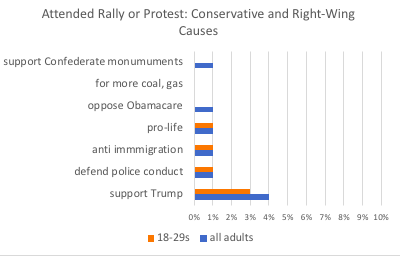
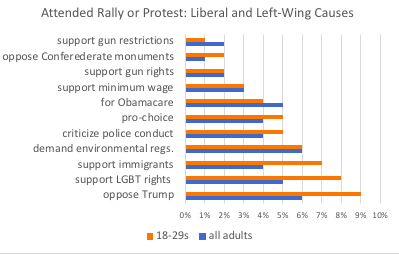





 Name: Katherine Roxlo
Name: Katherine Roxlo