I will present a paper entitled “An Association as a Belief Network and Social Network” at next week’s Midwestern Political Science Association meeting (remotely). This is the paper.
Abstract:
A social network is composed of individuals who may have various relationships with one another. Each member of such a network may hold relevant beliefs and may connect each belief to other beliefs. A connection between two beliefs is a reason. Each member’s beliefs and reasons form a more-or-less connected network. As members of a group interact, they share some of their respective beliefs and reasons with peers and form a belief-network that represents their common view. However, either the social network or the belief network can be disconnected if the group is divided.
This study mapped both the social network and the belief-network of a Rotary Club in the US Midwest. The Club’s leadership found the results useful for diagnostic and planning purposes. This study also piloted a methodology that may be useful for social scientists who analyze organizations and associations of various kinds.
Two illustrative graphs …
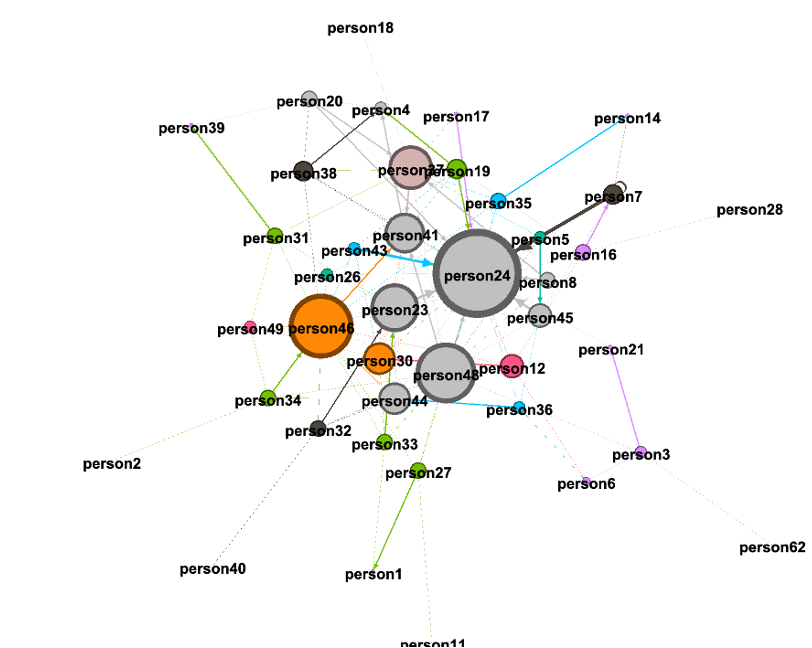
Below is the social network of the organization. A link indicates that someone named another person as a significant influence. The size of each dot reflects the number of people who named that individual. The network is connected, not balkanized. However, there are definitely some insiders, who have lots of connections, and a periphery.
The belief-network is shown above this post. The nodes are beliefs held by members of the group. A link indicates that some members connect one belief to another as a reason, e.g., “I appreciate friendships in the club” and therefore, “I enjoy the meetings” (or vice-versa). Nodes with more connections are larger and placed nearer the center.
One takeaway is that members disagree about certain matters, such as the state of the local economy, but those contested beliefs do not serve as reasons for other beliefs, which prevents the group from fragmenting.
I would be interested in replicating this method with other organizations. I can share practical takeaways with a group while learning more from the additional case.
See also: a method for analyzing organizations
The post An Association as a Belief Network and Social Network appeared first on Peter Levine.

